Healthbeauty123.com – A twisted knee injury occurs when a ligament, often the ACL, becomes stretched or torn. The ACL controls the twisting and forward motion of the shinbone and is vulnerable to injury when the knee is extended beyond its normal range. In rare cases, more than one ligament can be injured during a twisted knee injury. Even if only one ligament is injured, the condition can still cause pain and discomfort.
Twisted Knee Injury Diagnosis
The symptoms of a twisted knee vary from person to person, but they generally include a mild swelling of the knee, increased pain when walking or standing, or a limited range of motion. These symptoms usually appear one to two weeks after the injury, and treatment may include rest, bracing, physical therapy, or surgery. After a diagnosis of a twisted knee, Dr. Sampson will supervise the safe return to activity.
Another cause of pain in the knee is a torn meniscus. A twisting knee injury can result in a torn meniscus, which is attached to the tibia. Meniscus tears are painful and often have a locking sensation. The pain will be felt in the side of the knee where the injury occurred. It is much more common to tear the medial meniscus than the lateral meniscus.

Besides the popliteus muscle, other knee ligaments may be injured as well. The ACL is the main ligament that keeps the knee stable and serves important mechanical functions. It also serves as a joint position sensor. A twisting knee injury can occur when the knee is decelerating rapidly, changing direction, or being struck in the wrong direction. Further, this injury can also damage the ankle. The popliteus muscle will require surgery if the injured knee cannot be repaired.
The Best Types of Treatment for Twisted Knee Injuries
A pop in the knee is another symptom of a twisted knee. A swollen knee or pain is another symptom of a twisted knee. Treatment options include rest, activity modification, and physical therapy. Depending on the severity of the injury, your doctor may recommend a period of physical therapy and rest. The patient will be closely monitored by Dr. Sampson to determine what type of treatment would be best for their particular case.
A serious twisting injury usually occurs during sports. The combination of sudden changes in direction and speed is what causes serious damage. The twisted knee can cause damage to the menisci, the cartilage, and the ligaments that support the knee. Damage to the kneecap and tendons may lead to patellofemoral instability, which can cause painful sensation and muscle weakness. It may also cause patellar instability or a greater Q angle of the knee.
A 35-year-old male presenting with right knee pain two weeks after a trivial twisting knee injury suffered while walking on a slippery floor. He was initially treated by his general practitioner and advised to rest. However, the pain returned two weeks later and the patient could not fully straighten his knee. MRI findings revealed an effusion and generalized tenderness over the joint line. Range of motion was limited to 30 to 100 degrees of flexion.
Twisted Knee Injury Diagnosis Made with Various Tests
A twisting knee injury can also involve the Medial Collateral Ligament, which is the inside side of the knee. The MCL prevents the knee from collapsing inward and is most commonly injured during sports that involve quick side-to-side movements. Depending on the severity of the injury, a Medial Collateral Ligament sprain can range from a minor tear to complete damage. It can also occur when a player makes contact with the outside of the knee or twists an injured knee.
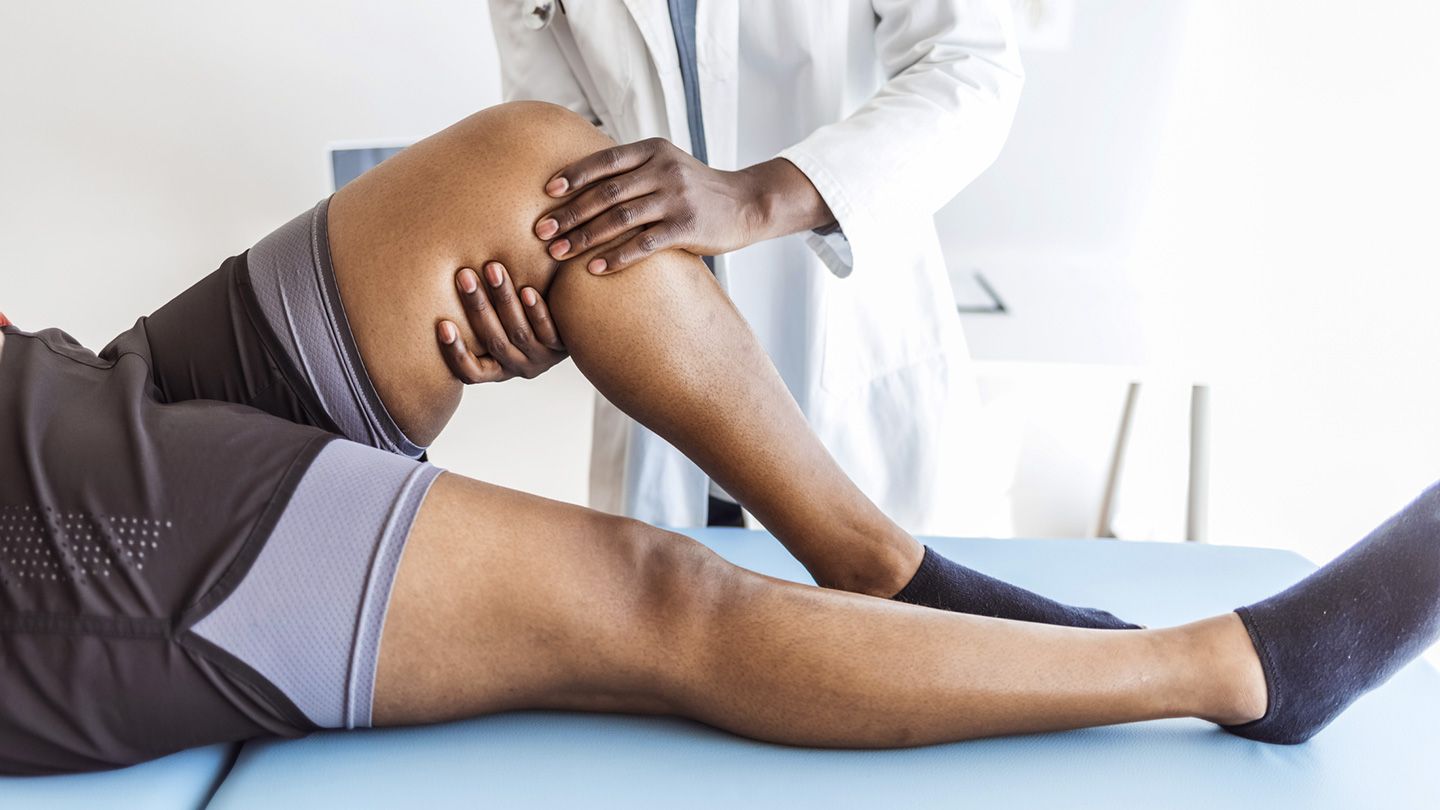
The diagnosis of a twisted knee injury can be made with a variety of tests. MRI is an imaging test that utilizes large magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of the knee joint. It can also reveal damage to surrounding tissues, ligaments, and muscles. A doctor’s treatment plan depends on the specific symptoms, age, and overall health of the patient. However, it is important to note that a patient should undergo a thorough examination before beginning treatment.
Reference:
Dickinson, F. L., W. M. Harper, and D. B. Finlay. “Knee tumours–duration and nature of symptoms prior to investigation.” The British Journal of Radiology 70.834 (1997): 635-637.






