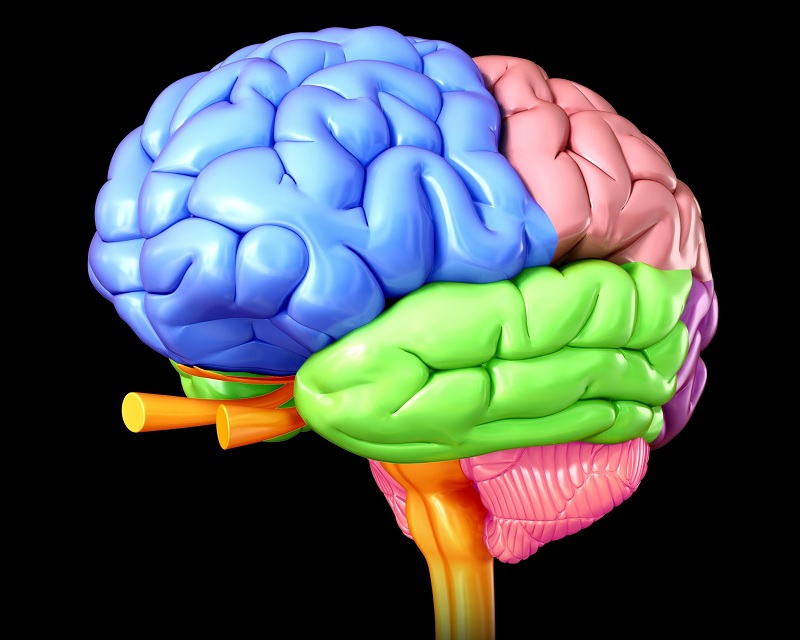
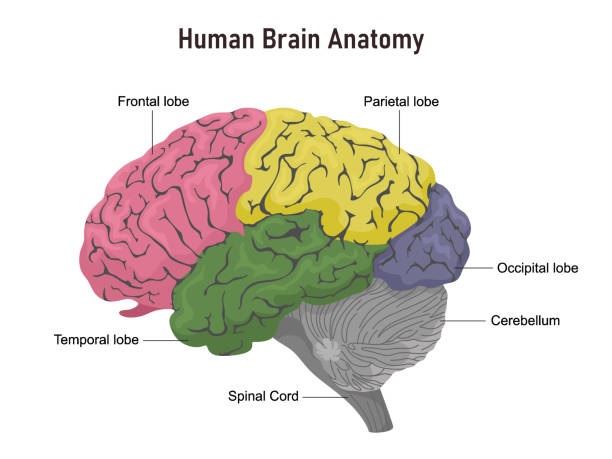
Healthbeauty123.com – The Right Posterior Frontal Lobe is one of the largest cortical structures in the brain. It is divided into two parts by two sulci: the olfactory sulcus and the middle temporal sulcus. The olfactory sulcus separate the medial and posterior orbital gyrus rectus.
Frontal Lobe Dysfunction Has Difficulty Motor Skills
There are many disorders that affect this area of the brain. People with frontal lobe dysfunction may experience difficulties with executive function and attention, change in personality and emotional state, or have difficulty with motor skills and spatial reasoning. Individuals with a disorder of this region of the brain may also experience changes in their motor and cognitive skills. For example, they may develop reduplicative paramnesia, a condition that causes a person to think that their home is identical to another location.
This disorder may result in immoral decision-making. This lobe controls the executive function of a person. It is responsible for personality, motivation, and decision-making. It also plays an important role in determining the individual’s emotional state. There are other types of disorders affecting the frontal lobe, including those that affect attention and executive function. Some people with a disorder of the right frontal lobe may experience sudden dramatic changes in their emotions and personality.
In the bipolar AP EEG, the interictal spike is observed at the V4 and V6 of the right frontal lobe. Afterward, the spikes are located in the V9 and V10 of the right parietal lobe. The time-based view shows that the MEG-based onset occurs in the midfrontal lobe and is recurrent in the right occipitotemporoparietal lobe.
The Frontal Lobe Occupies One-third of the Cerebral Hemisphere
An ischemic stroke is caused by a disorder in the right hemisphere. The frontal lobe occupies one-third of the cerebral hemisphere and extends posteriorly from the most anterior part of the skull to the Sylvian fissure. Its lateral sulcus separates the right frontal lobe from the temporal lobe. The lateral sulcus marks the inferior and posterior borders of the frontal limbs.
Patients with this syndrome typically have cognitive, behavioral, and social behavior problems. They may display a range of emotional and cognitive symptoms, such as impulsivity, impulse control, and memory. They may also have a disorder of the frontal lobe. As a result, it is important to educate family members about the condition and how to care for the patient. The patient will most likely experience a gradual loss of their abilities.
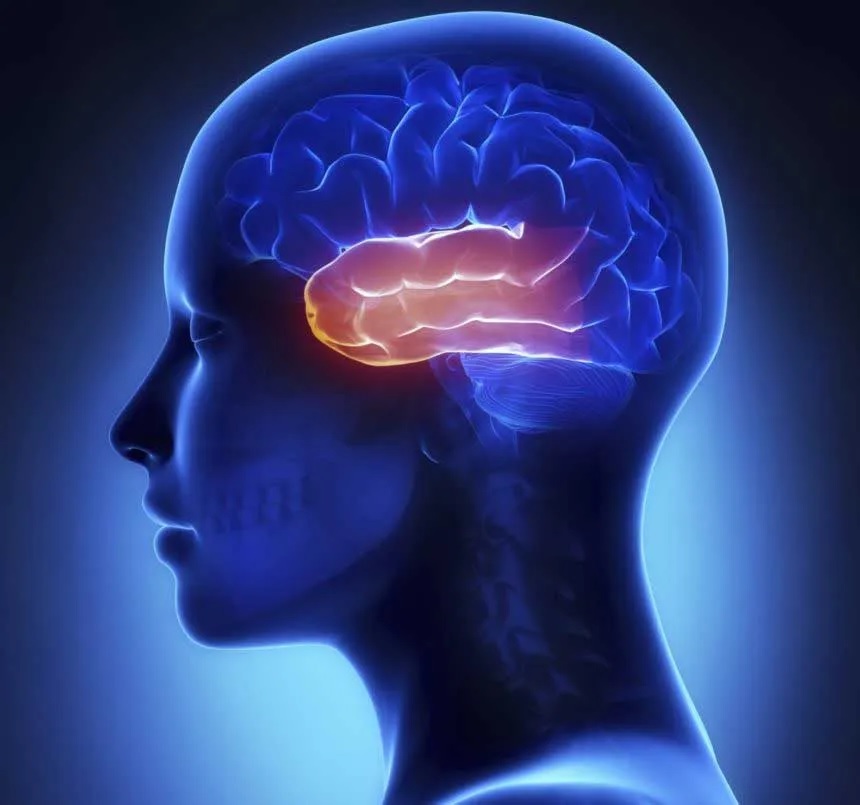
The diagnosis of Right Posterior Frontal Lobe syndrome depends on the underlying pathology and symptoms. The earliest onset was in the left occipitoparietal junction, lateral to the MRI lesion, and then spread to the surrounding VS areas and the left posterior frontal lobe. In this syndrome, the onset is asymmetric and the patient will likely lose his or her ability to walk.
Neuropsychological Evaluation can Assess the Severity of the Condition
Neuropsychological evaluations can assess the severity of the condition. This includes speech, social behavior, and memory. Other tests assess the ability to perform tasks requiring cognitive, motor, and emotional abilities. The Right Posterior Frontal Lobe can also be damaged due to a wide range of diseases. In severe cases, the symptoms of a stroke will affect the patient’s ability to remember familiar places.
The symptomatic MRI scan of the subject’s right frontal lobe revealed a tumor resected in this lobe. An ECoG showed that the tumor had spread to adjacent VS areas, including the left posterior frontal lobe. An ECoG revealed the presence of four orbital gyri in the right posterior of the lobe.

The right posterior frontal lobe is the most common part of the brain. It is connected to the cingulate gyrus, which is an anaplastic nerve cell. The posterior frontal lobe is the most sensitive part of the human brain, and is the most important. Acute sulcus may be the cause of a glioma, a type of cancer.
Reference: