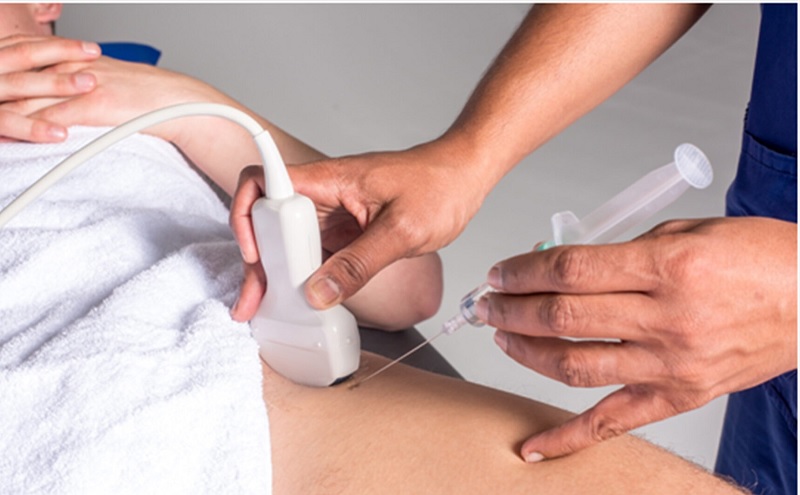
Healthbeauty123.com – In patients with suspected periprosthetic joint infection (PJI), hip aspirations are usually performed using fluoroscopy or ultrasound guidance. However, a recent study has evaluated the effect of anatomic landmarks for aspiration. The authors retrospectively reviewed 186 consecutive hip aspirations. The majority of patients had an underlying periprosthetic joint infection, and the authors were aiming to locate the puncture site two to three cm lateral to the femoral artery pulse and the inguinal ligament.
Hip Aspiration Procedure for Acute and Chronic Infection
In the study, hip aspiration procedures were performed for suspected acute and chronic infections in a cohort of 319 patients. The median time from surgery to hip aspiration was 319.4 days and 27.6 days, respectively. One-third of the patients undergoing hip aspiration underwent a saline lavage. Tables 1 and 2 summarize the differences between the cohorts. This study found that there was a significant correlation between patients’ age, femoral head size, and type of infection.
Although this study was conducted on an entire population, its retrospective design may have limited its power. Many patients with hip aspirations performed under ultrasound guidance had incomplete medical records, which may have hampered statistical analysis of surgical factors. Furthermore, antibiotic use in the study population was not easily accessible. Additionally, all patients who had antibiotic cement spacers were excluded. Overall, the study was an excellent tool for performing hip aspiration on patients with suspected PJI.
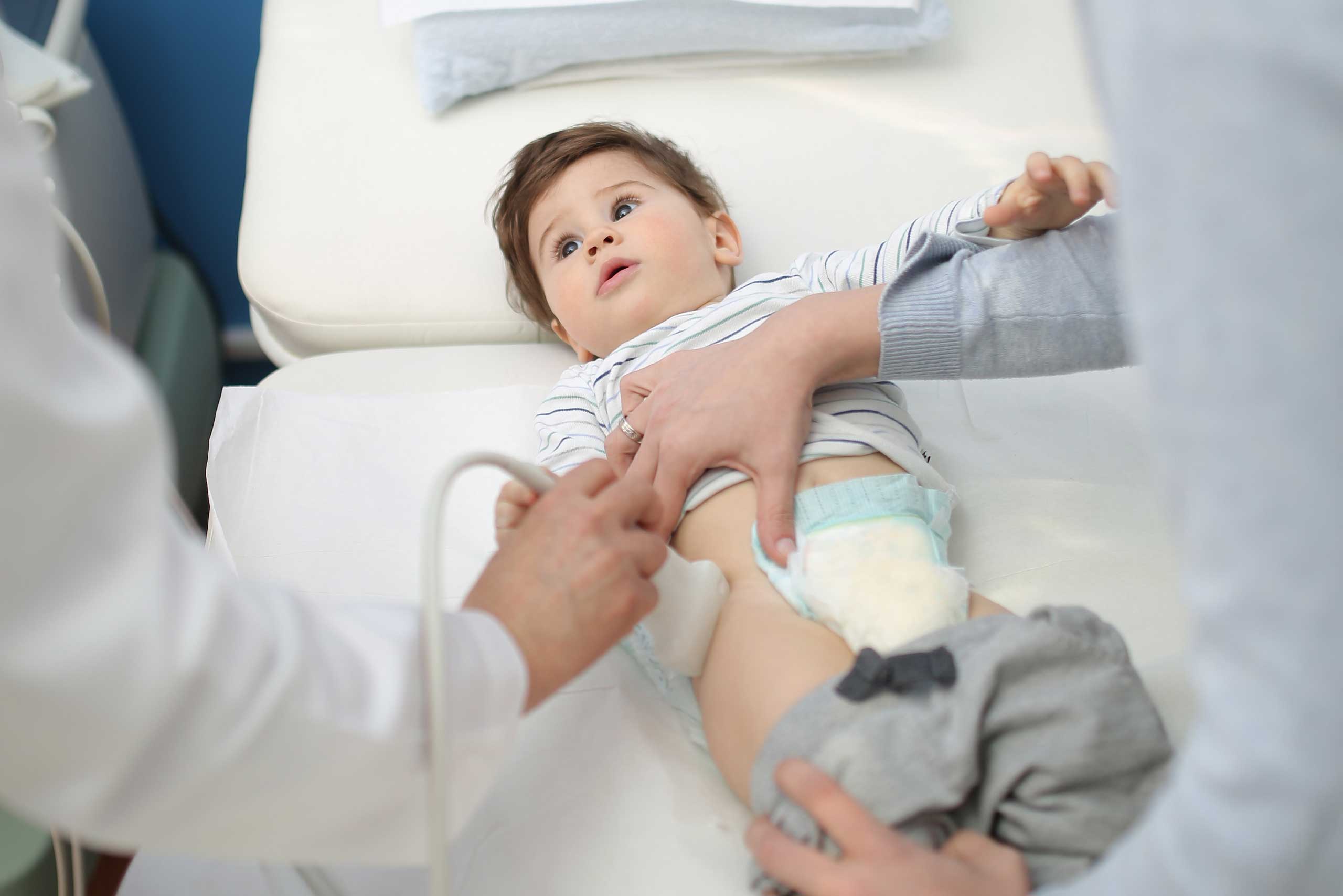
Ultrasound-Guided Hip Aspiration Technique
The Mayo Clinic have implemented an ultrasound-guided hip aspiration technique. This technique allows for a better yield of synovial fluid and less radiation exposure. Traditional fluoroscopy is not as accurate for imaging soft tissues, and ultrasound-guided aspiration offers greater convenience for patients. In addition, ultrasound-guided aspiration is less invasive, which is great news for patients. You can even do it at home, which is an added bonus.
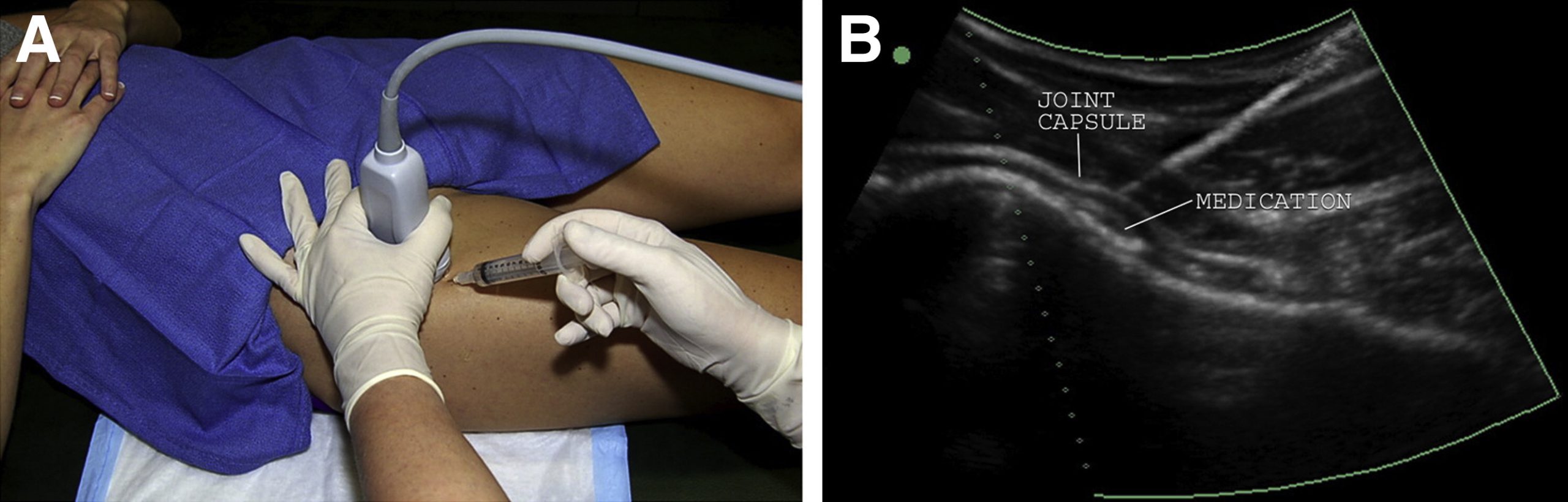
Moreover, there are a number of major indications for joint aspiration. Among them are hemarthrosis, bursal effusion, and monoarthritis. This procedure also relieves the patient’s discomfort and allows them to bear weight on the affected joint. Joint aspiration can also be performed for other reasons, including intra-articular medication. It is important to perform this procedure under strict sterile conditions to reduce the risks of permanent damage.
Procedures that Remove Fluid from the Joints
Joint aspiration, also known as arthrocentesis, is a procedure that removes fluid from joints. The fluid obtained from this procedure is used to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or bursitis. Depending on the results of the aspiration, the fluid can be sent to a laboratory for tests or diagnosis. It may contain corticosteroids to treat conditions or improve pain.
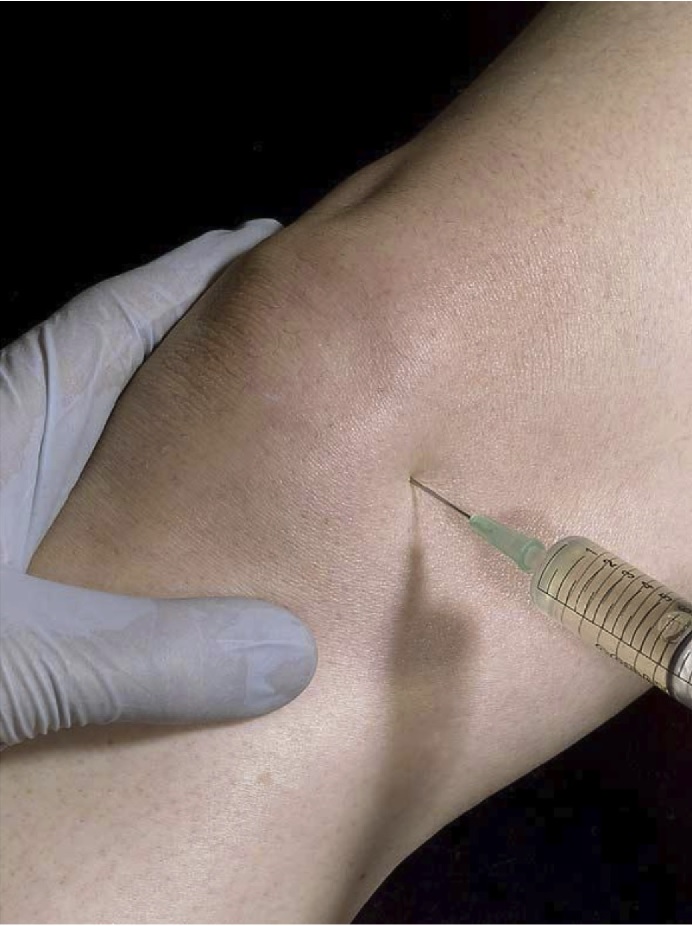
To perform this procedure, the needle is inserted through the skin at a slightly stretched angle. Some physicians also inject lidocaine into the skin to minimize the pain associated with needle insertion. The needle is usually inserted a distance of one to four and a half to one-and-a-quarter inches from the knee joint. To make the procedure easier, a nondominant hand may be used to help the physician insert the needle.
Reference: