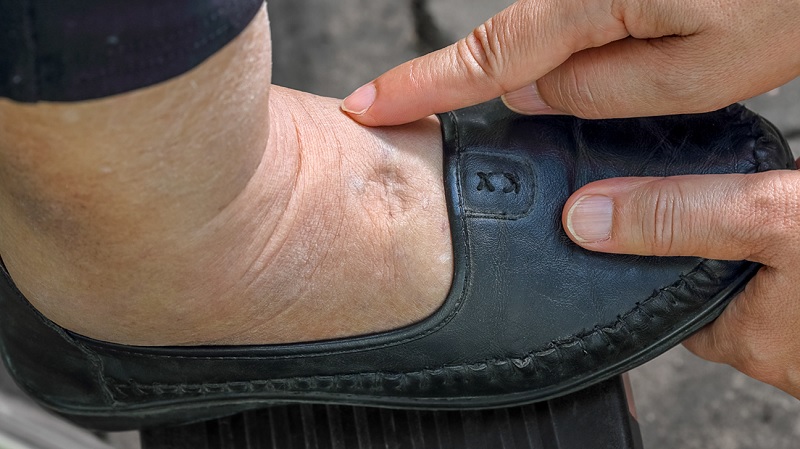
Healthbeauty123.com – There are several symptoms of peripheral edema that you should be aware of. The affected area will be swollen, painful, and may be bruised. The skin around the affected area may also be shiny or warm to the touch. Painful tension will also be felt in the affected area. Chest pain is a symptom of peripheral edema. Seek medical care for this condition as soon as possible.
Symptoms of Peripheral Edema Varies
The symptoms of peripheral edema will vary depending on the cause. The most common symptom is a swollen area that feels warm and strains. It may also appear bruised or discolored due to an injury. Other symptoms include skin discoloration, stiffness, difficulty walking, and an elevated heart rate. There is a high risk of developing peripheral edema if the edema is not diagnosed.
There are several reasons why people develop peripheral edema. Inactivity, a poor diet, hormone changes, and a sedentary lifestyle can all contribute to water retention. Also, being overweight and taking certain medications can increase your risk. You can reduce your risk of developing peripheral edema by staying active and reducing your salt intake. Elevating the affected area may also be helpful.
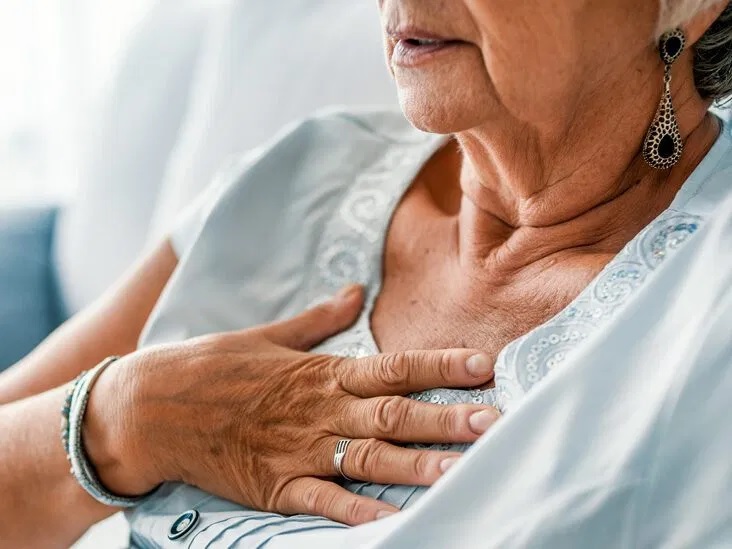

Treatment for peripheral edema will depend on the cause of the condition. Your physician will perform a thorough physical examination and urine test to identify the cause of fluid retention. A treatment plan may include a diuretic or limiting salt intake. You may also want to try essential oils like grapefruit and fennel, which help reduce water retention. Further, massaging the affected area will lower the pressure on the blood vessels.
Medical Conditions in which Fluid Accumulates in Tissue
What Are the Peripheral Edema Symptom? Peripheral edema is a medical condition in which fluid collects in tissues. The affected area becomes painful and heavy. The symptoms of peripheral edema are not the same in all patients, but maybe indicative of more serious conditions. Some people with peripheral edema have liver cirrhosis or kidney disease, as well as congestive heart failure.
Medicare does pay for peripheral edema treatment. A separate 10 percent rating is needed for each lower extremity. Hence, a separate disability rating should be provided for peripheral edema of the lower extremities. The lower extremities should also be rated separately, since the right lower extremity has a higher risk of swelling than the left one. These are the key factors to consider when applying for disability compensation for peripheral edema.
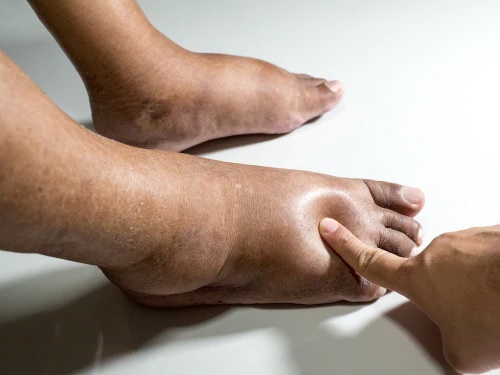
A VA examination report reveals that the Veteran has significant edema in both legs. Consequently, the edema is likely the result of hypertension treatment. Several medical reports document the Veteran’s complaints of pain and swelling in his lower extremities. Furthermore, the VA examination reports show that peripheral edema is a specific symptom of hypertension. The Board also considers his history of hypertension as a factor in the onset of the peripheral edema in his lower extremities.
Natural Remedies for Patients with Peripheral Edema
There are many natural treatments for peripheral edema. Parsley is a natural diuretic that triggers the kidney to produce urine. This helps rid the body of excess water, which causes peripheral edema. Parsley extract powder is available as a dietary supplement. It should be taken according to a physician’s orders. Dandelion root can also increase your frequency of urination. Dandelions are effective in treating edema and can be taken as a supplement in dosages of 1,000 mg twice daily.

The Veteran is entitled to a separate disability rating for left lower extremity peripheral edema resulting from his service-connected hypertension. The veteran is also subject to VA laws and regulations related to payment of benefits. For further information, read his VA examination report and review the patient’s medical records. This information can be invaluable in determining whether this symptom is indeed caused by hypertension. There are several other symptoms that indicate the presence of peripheral edema, including a high blood pressure and an increased tendency to swell when the feet are wet.
Reference: