Healthbeauty123.com – The radiologist uses radiographic imaging to diagnose and treat gout. Radiographs of the joints can be used to detect urate crystals in the periarticular space and intraarticular space. Dual-energy computed tomography (DECT) is a common diagnostic technique used for gout. It can also help in the diagnosis of nephrotic syndrome, which is associated with a lower risk of gout.
Sensitive Imaging Modalities for Gout
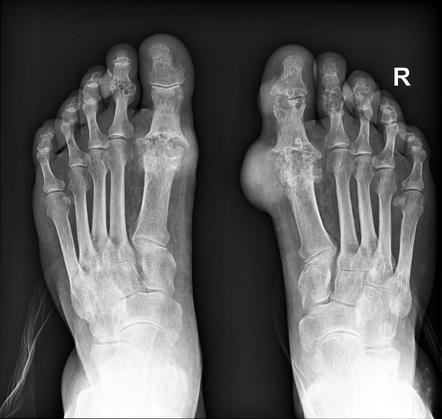
Contrast-enhanced CT is a sensitive imaging modality for gout, but its high cost and radiation levels prevent routine use. It is relatively accurate and sensitive, and it can detect small tophi that may be radiographically undetectable. Tophi typically appear as overhanging margins in the joint and opacity over the entire area. Tophi can be found in the intra-articular space as well as in subcutaneous tissues.
During the early stages of gout, symptoms are restricted to soft tissues. On plain-film radiographs, patients may have edema or asymmetric swelling around the affected joint. The affected joint may appear cloudy on MRI, especially if there are multiple episodes of the disease. If the swelling or edema is severe, the patient may have a fracture. However, MRIs can provide a clear picture of the underlying disease and help determine the best course of treatment.
Ultrasound is an important diagnostic tool in gout. The study authors suggest that it is a better option than conventional X-ray. Moreover, the high resolution of ultrasound allows doctors to identify bone morphology in the affected joint. Further, CTs are more precise than plain radiographs in detecting the presence of crystals. This imaging method may be able to detect early gout due to its ability to provide detailed images.
Identifying Urate Crystals in the Extra-articular or Intra-articular Area
A CT provides more detailed images than a plain radiograph. It can identify urate crystals in the extraarticular or intraarticular area. A CT without contrast may be more useful in gout, while an MRI without contrast may not be helpful in early stages. A DECT can also help detect urate crystals by their chemical composition, making it a valuable tool in the diagnosis and treatment of gout.
CT can provide detailed images, which are more accurate than plain radiographs. It can show uric acid crystals in the extraarticular area and bony erosions in the intraarticular space. It can also provide detailed images of the soft tissues, which may not be visible on plain radiographs. The scan can also detect uric acid and other substances present in the joint fluid. If a patient has a history of gout, he or she should consult a physician.
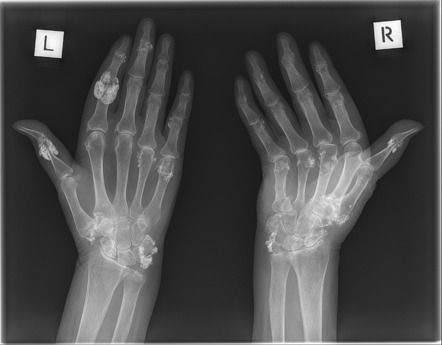
A DECT scan is an imaging method that uses a dual-source scanner to obtain images of gout. A DECT image is a good example of gout, because the DECT image shows tophi and MSU deposits. A DECT scan can show the four main elements of gout: uracilatous deposits, cartilage damage, and bone erosion. It can also show calcification in a joint, which is important for treating gout.
Choosing the Most Appropriate and Best Treatment
The usual imaging findings in gout include tophus, aggregates, and erosion. Several imaging studies are available that can help determine the severity of the disease and help doctors choose the most appropriate treatment. Usually, a doctor will refer patients to a specialist if he or she has concerns about gout. An ultrasound of a joint is a good way to diagnose gout. It can also show signs of the various stages of the disease.
A patient with gout is examined for the presence of urate crystals in the periarticular soft tissues. Typical radiographic findings include the presence of a needle-shaped crystal in the bone tophus. In contrast, a CTA is not recommended because the patient cannot tolerate formalin. A biopsy is the only way to confirm the diagnosis of gout. It is important to perform a complete and unbiased autopsy.
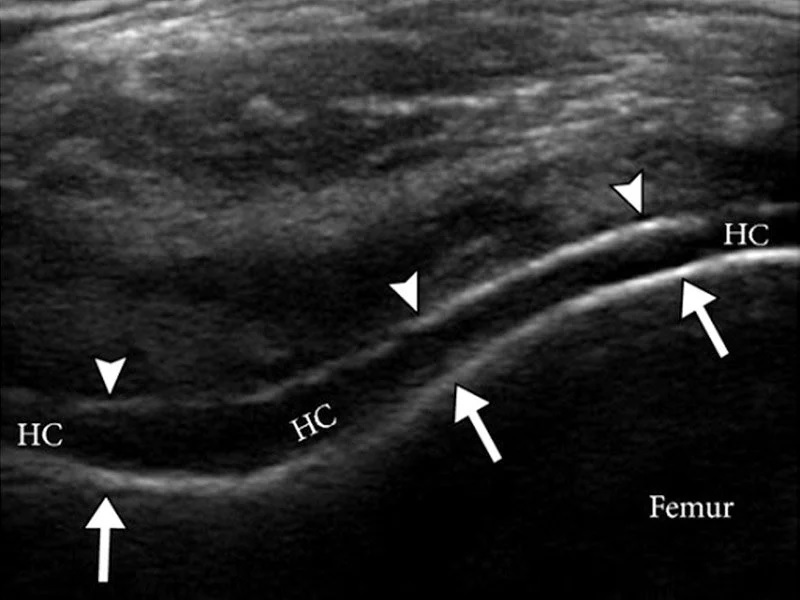
Ultrasound imaging of the joint can help in the diagnosis of gout. Tophi can be seen in the articular cartilage, fingers, and joints. Moreover, a sensitivity of 56% has been reported for this test. Among physicians, a high sensitivity of tophi reveals the presence of tophaceous gout. A high sensitivity of tophi is found in patients with anorectic gout, but it is not always definitive.
Reference:






