Healthbeauty123.com – If you’ve ever wondered how your body moves, this Anatomy and Physiology joint lesson will help you understand how your joints function. Joints allow muscles to pull on adjacent bones, which produces movement. Motions that are possible at joints include gliding, rolling, and approximation. Joints also provide support for our bones, and are essential for our daily activities. Learn about the different types of joints and what they can do for you.
Joint Anatomy and Physiology Are Divided Into Three Basic Types
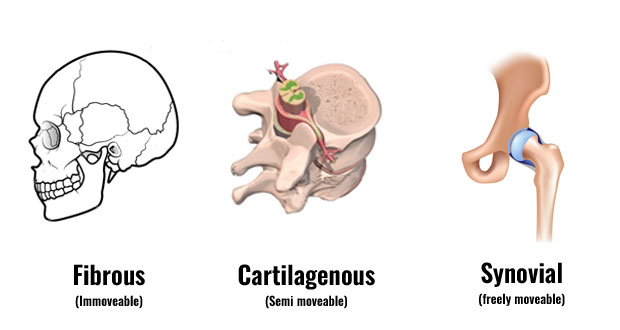
Anatomy and physiology Joints are divided into three basic types. Fixed joints have no movement, while movable joints can move slightly. Fibrous joints are called synarthroses, while cartilaginous joints are called amphiarthroses. Joints that allow some movement are called diarthroses, and include the shoulder, elbow, ankle, and wrist. Finally, there are the nonmoving joints, or gomphoses.
Arthritis is an example of a degenerative joint disease, or arthritic. This condition is characterized by gradual wear and tear of joint cartilage, with inadequate repair. According to their structure, joints can be classified as fibrous, cartilaginous, or synovial. All three types of joints can cause pain and limit movement. The type of joint affected depends on the severity of the injury.
The human body consists of 206 bones, each connected to at least one other bone. These bones move due to skeletal muscles attached to them. Each individual has 206 bones in their skeleton, but the amount varies from person to person. A baby starts with about 270 bones, but some are fused together during growth. An adult has 206 named bones and 80 in the axial skeleton. In addition, there are 126 bones in the appendicular skeleton. Overall, the human body contains 250 to 350 bones.
The Last Two Types of Joints Characterized by Limited Mobility
The other types of joints are amorphous or fluid-filled. These are composed of cartilage, while the latter are made up of a dense layer of fibrocartilage. The latter two types of joints are often characterized by limited mobility. If a joint has limited mobility, it is called a “fibrosis” or arthrosis. It is possible to have amphiarthrosis, which is the opposite of the aphthous joint.
Bones and cartilage are made up of two kinds of joint. These are called articulations and connect adjacent bones with a ball or sphere. Joints are further classified according to the type of connective tissue. Cartilage and fibrous tissue connect adjacent bones, while cartilage and hyaline cartilage are joined together. Synovial joints have articulating surfaces in a fluid-filled joint cavity.
A pivot joint is an articulation between two bones with similar radii. These joints allow for two axes of motion. Examples of pivot joints are the proximal radioulnar joint and the atlantoaxial joint. The axis articulates with the inner aspect of the atlas and is held in place by a ligament. Movement at the atlantoaxial joint is also possible.
Common Movements That Allow Various Body Movements
A common motion that allows for various body movements is circumduction. This is a circular movement with one end remaining relatively stationary and the other end moving in an outward direction. In addition, flexion and extension are always described in relation to anatomical positions. For example, flexion is the movement that bends the head or shoulders, while extension is the motion that straightens it. The extension is the opposite movement, whereas abduction is the movement away from the body. Adduction involves spreading the fingers or toes toward the rear of the body.
Synovial joints are the most common type of joint in the body. Synovial joints are filled with synovial fluid. These joints are surrounded by an articular capsule, which is a fibrous connective tissue that is attached to the participating bone at just beyond the articulating surface. Articular cartilage covers the articulating surface, and the synovial membrane is lined with articular cartilage.
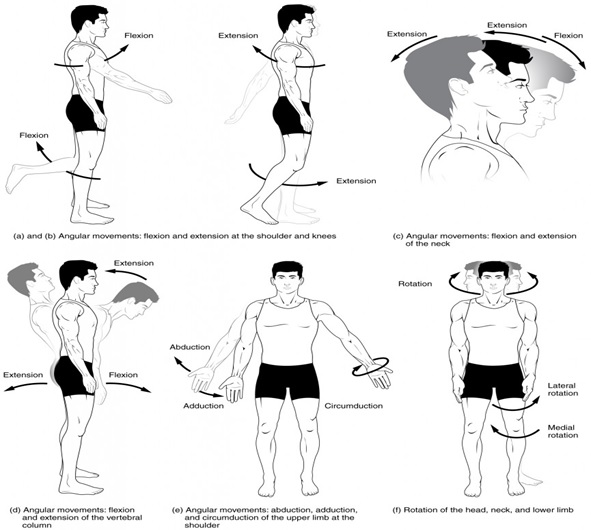
Ball and socket joints allow side to side, backward, and rotational movement. These joints are found in shoulder and hip joints. Condyloid joints allow flexion and extension. They are found between the phalanges and metacarpals. They can also be found in the hip and finger joints. The types of joints in the human body differ based on their function. For example, ball and socket joints can be very flexible, while hinge joints are stiff and unmoving.






