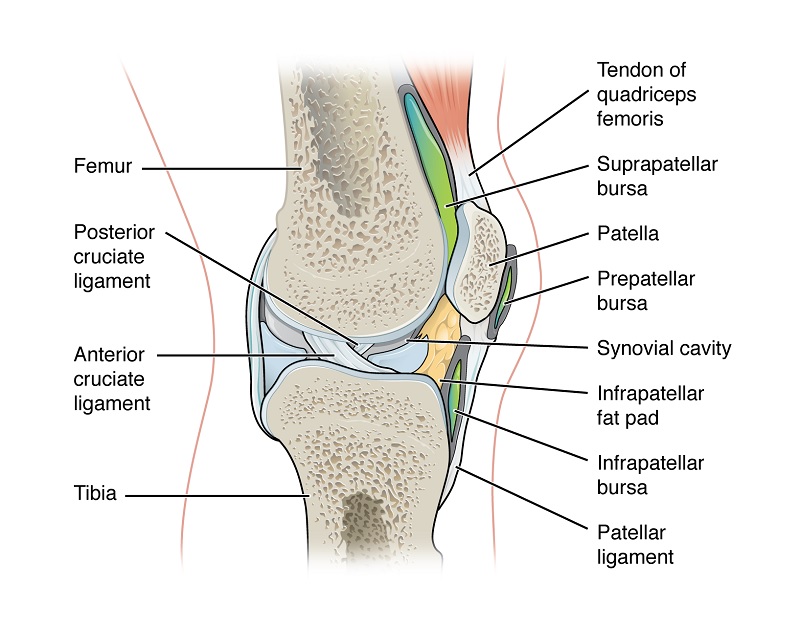
Healthbeauty123.com – A synovial bursa is a small fluid-filled sac lined by a synovial membrane. It contains a layer of viscous synovial fluid that provides a cushion between bones. Bursae surround the majority of the major joints of the body, and they are particularly important for movement. The authors review the current state of knowledge about synovial bursae and discuss how to reconcile differences in clinical and anatomical terminology.
Inflammation of the Synovial Bursa
The fluid within the bursa serves two main functions. It helps to reduce friction in joints and serves as a shock absorber. It also helps to distribute nutrients throughout the body. When bursa fluid is irritated, it’s referred to as bursitis. Inflammation of a synovial bursa is a hallmark of arthritis. Here are some common symptoms associated with inflammation of the synovial bursa.
The synovial membrane is the soft tissue that lines the joint cavity and articular capsule. The membrane contains a clear lubricating fluid called synovial fluid. The outer layer of the bursa is either fibrous or fatty, or it may be loosely areolar. The inner layer of the bursa is made of a sheet of cells, forming a layer that is thinner than a piece of paper.

When diagnosed, treatment will depend on the severity and duration of the bursitis. Conservative measures may be enough to reduce symptoms and help you return to normal activity. More invasive treatments may be necessary if bursitis persists longer than six weeks. The first step is to consult a doctor. The treatment you choose will depend on the condition and your overall health. In some cases, surgery is the only option, but it’s generally not a necessary one.
Three Types of Exchange
There are three types of bursa: subcutaneous, adventitious, and synovial. The subcutaneous bursae are situated between the skin and bony prominences. The subcutaneous bursa is typically one to three millimeters thick. However, they vary in size between individuals and their location in the body. Symptoms of bursitis may include pain, tenderness, or inflammation of the joint.
While the symptoms of bursitis may resemble those of other diseases, the treatment will depend on the underlying cause of the condition. The most common causes of bursitis include injury, repetitive friction, and underlying disease. The following are some treatments for bursitis. So, don’t delay treatment! And be sure to visit your doctor if you experience any symptoms. It’s worth knowing the difference between bursitis and other forms of arthritis.
The navicular bursa is a true synovial bursa located between the distal scutum and deep digital flexor tendon. It has an outpouching that extends almost to the distal end of the digital flexor tendon shea. Its size is large enough to diffuse medication and local anesthesia into the joint. It’s a highly important part of the body’s anatomy and can lead to severe lameness in the foot.
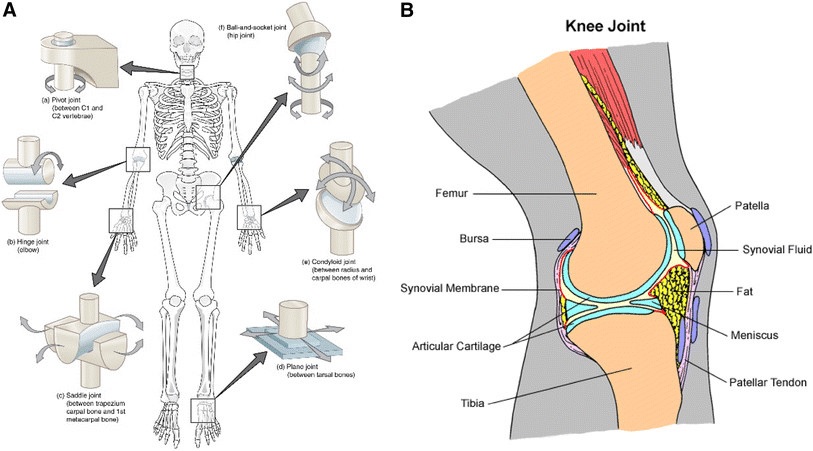
Synovial Joints in the Body
There are several types of synovial joints in the body. One of the most common is the acromioclavicular joint, which is made up of a scapula, a clavicle, and several condyles. A synovial joint is usually flat and provides gliding or slipping properties. If the joint is synovial, it is a type of arthroscopically operated jointly.
A synovial joint is a flexible joint that consists of articulating bones and a synovial capsule surrounding the joint. Synovial fluid lubricates the joint and reduces friction during movement. The capsule surrounds the articulating bones and is typically associated with accessory ligaments. A synovial bursa can be a sign of diarthrosis, which is a condition involving a joint that is not properly functioning.
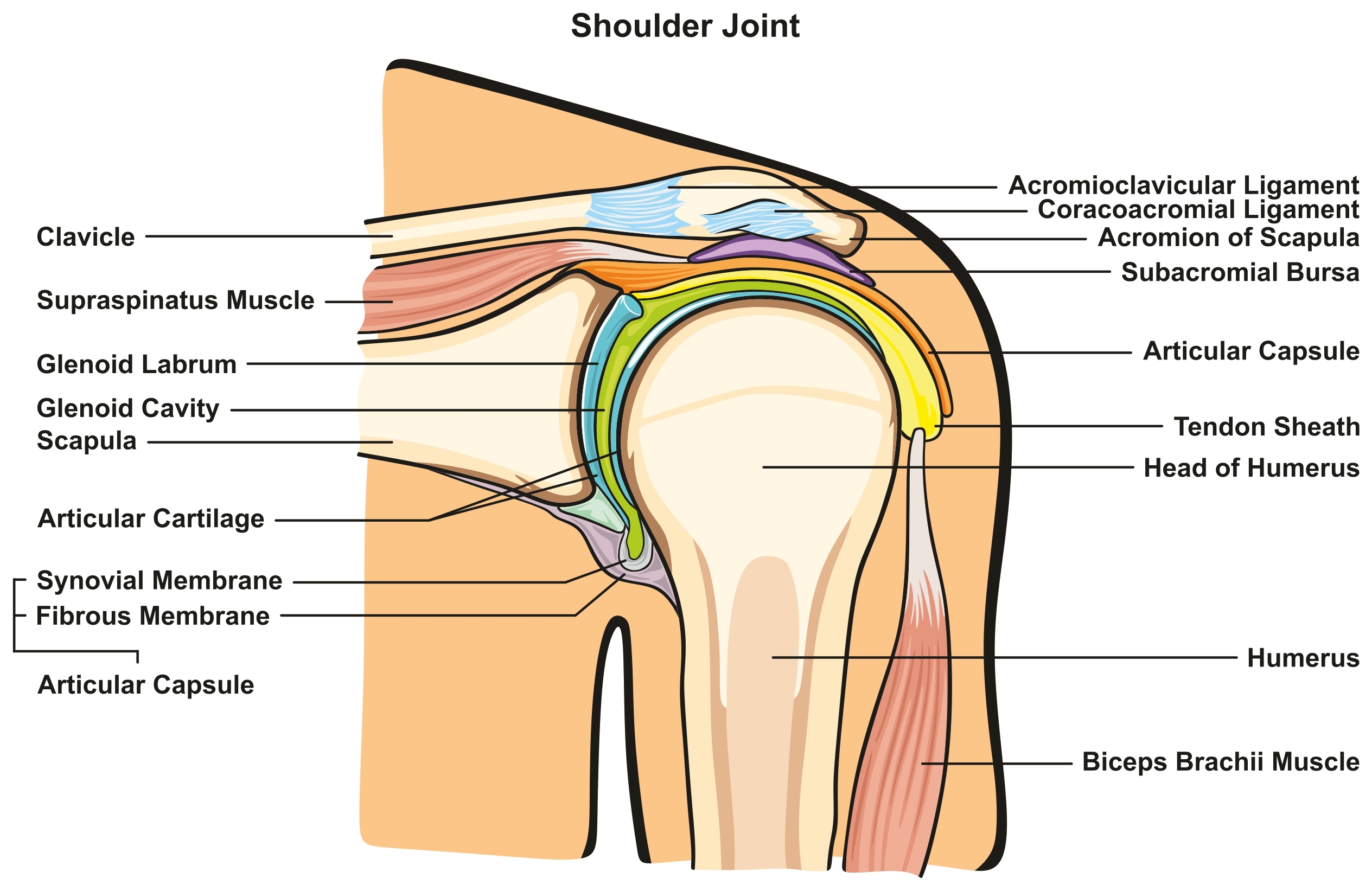
Both conditions may be present at the same time, and healthcare providers can tell if a patient has one or the other by looking at imaging tests. Often, these patients have both conditions. During an initial visit, the healthcare provider will discuss both possible diagnoses to determine which one will occur in the patient. The pain will indicate which one is more serious, and imaging tests will help determine which one should be treated first. If the patient’s condition requires surgery, treatment may be necessary.
Reference: