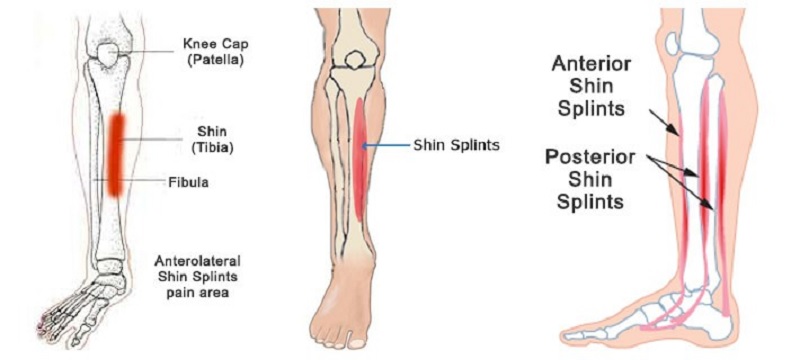
Healthbeauty123.com – A Shinbone Fracture can occur in either leg. A physician may recommend x-rays for the diagnosis. The x-rays may show a tibial shaft or fibula fracture. A doctor will also order a CT scan to determine the extent of the fracture. A CT scan can be helpful in determining whether a break needs to be repaired. The doctor will use the x-ray results to determine the type of treatment needed.
The Goal of Treatment is to Keep the Bones in the Right Position
There are two primary treatment options for a shinbone fracture. The first involves placing a metal rod into the central canal of the tibia and securing the nail across the fracture site. The metal rod is screwed into the bone to hold it in place while the bone heals. The second procedure is known as external fixation. This procedure involves screwing or pins into the bone and attaching the bone to a bar on the outside of the skin. The goal of both treatments is to keep the bones in their proper positions while healing.
The third method of treatment involves surgery. In a surgical procedure, a bone is pounded against another bone. In a shinbone fracture, the bone pieces are secured with sutures. This type of treatment is often done on children and does not require surgery. Patients usually stay in the recovery room for two hours after a shinbone fracture. They will be given enough pain medication and given instructions on how to recover. They will be given a prescription for pain medicine and are given a follow-up appointment for their follow-up visit.
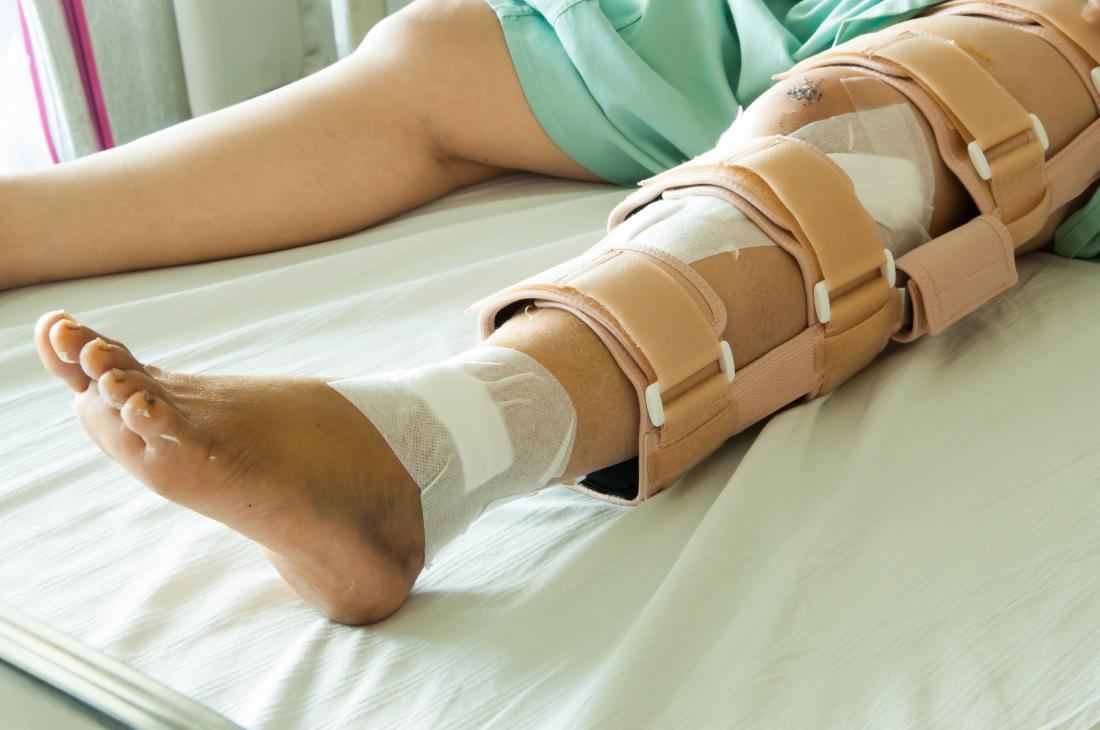
A splint may provide support for the broken shinbone until the fracture heals. In some cases, a functional brace is used to immobilize the injured extremity during the initial healing process. A plastic or fastener-based functional brace provides support until the healing process is complete. However, these braces can be removed for physical therapy and personal hygiene. They are typically reusable, which makes them a convenient option for many people.
Early Symptoms of Dry Bone Injury
A non-displaced tibia fracture occurs when the bones stay in the same position. This type of shinbone fracture is often a result of a twisting or mild traumatic event. A shinbone injury is usually accompanied by pain, swelling, and loss of mobility. While a shinbone is usually not dangerous or painful, it can be painful. The initial symptom of this fracture is limpness. A physician may prescribe ice or a cast.
A shinbone fracture is often painful, and it is common for patients to spend an overnight stay in the hospital. During the early recovery phase, physical therapy for a shinbone fracture should focus on increasing the range of motion in the knee. Once the bones heal, a functional splint may be used to protect the affected shinbone. After the splint is removed, a patient can return to their usual activities.

Treatment of a shinbone fracture depends on its severity. Nonsurgical treatment involves immobilizing the fractured extremity. The patient will be placed in a splint for the first few days until the fracture heals. The patient will be required to take x-rays on a regular basis to assess the healing process. A splint can be removed for personal hygiene and physical therapy.
Wearing a Functional Support for a Fractured shin
A splint will provide support for the fractured shinbone. The splint will be adjusted to allow for swelling. A cast is immobilized until the bone heals. Once the bone has healed, it will need to be reinserted. The splint will be removed for hygiene and physical therapy. A cast can cause more damage to the surrounding tissues. It may be necessary to wear a functional brace for two to three weeks until the bone has completely healed.
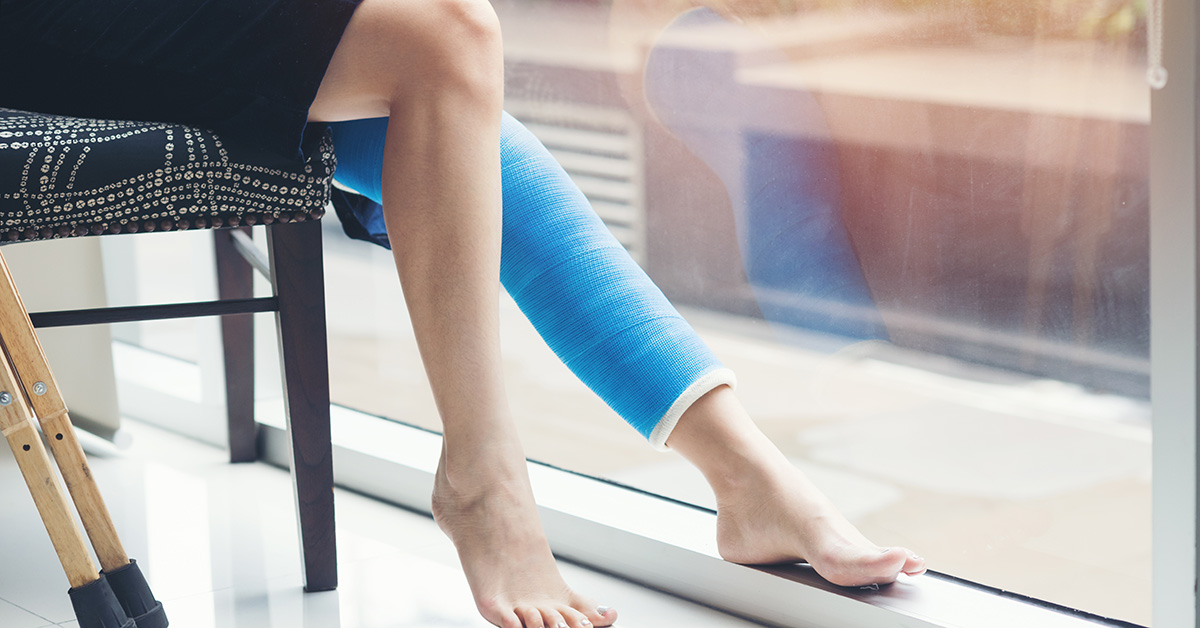

A nondisplaced fracture is a common injury in children under the age of 4. It may be the result of a minor twisting injury or a simple fall. A child with a nondisplaced shinbone will likely have a limp for the first few weeks. An X-ray or CT scan will also help determine if the shinbone fracture is open. A splint will protect the affected area while it heals.
Reference: