Healthbeauty123.com – Bronchial arteries vary in number and origin, but they all originate from the descending thoracic aorta. In approximately 70 percent of humans, bronchial arteries arise from the T5 or T6 vertebral body. The most common artery is the right intercostobrachial trunk. These arteries supply the chest wall and originate from the posteromedial aorta.
Four Major Bronchial Arteries in the Human Body
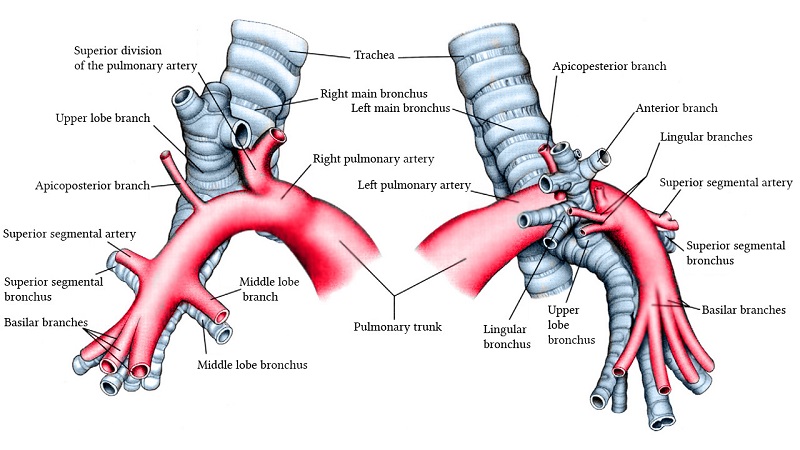
There are four major bronchial arteries in the human body, each providing arterial blood supply to the trachea and bronchi. The bronchial arteries form an anastomose with the pulmonary artery and provide blood to the connective tissue of the lungs and viscera. They also supply the aorta and pulmonary vascula. Each lobar and segmental rib contains two bronchial arteries.
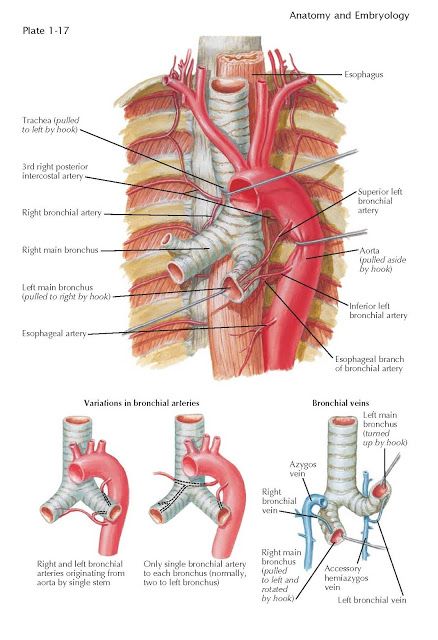
Unlike the coronary arteries, bronchial arteries lack veins. They are thought to be “nutrient” vascular systems for the pulmonary tissues. Branches of these arteries include the superior vena cava, the azygos vein, and the third posterior intercostal artery. The bronchial arteries run on the posterior surfaces of the bronchi, and they interconnect with the pulmonary arteries to supply the mediastinal structures.
The bronchial artery has three main branches: the superior and middle bronchial arteries. These arteries also supply the orifices of the secondary bronchi. Pigeons have one true bronchial artery, with no branching to exchange tissue. They are also referred to as pulmonary artery limbs. These arteries provide a pathway to the extrapulmonary tissues of the respiratory system.
The Type of Pulmonary Artery is Anastomotic
The bronchial artery branches to the anterior spinal artery, which supplies the spinal cord. The right bronchial artery, meanwhile, feeds the great anterior radicular artery and radiculomedullary artery. The artery may branch to other arteries, resulting in transverse myelitis. The two types of pulmonary arteries are anastomotic.
The bronchial artery is a vascular system that supplies the mediastinum. The right pulmonary artery provides drainage to the left side of the heart. The left bronchial artery supplies extrapulmonary blood to the right heart. The two sides of the lungs are connected via the azygous artery. However, the azygous vein also connects to the aorta.
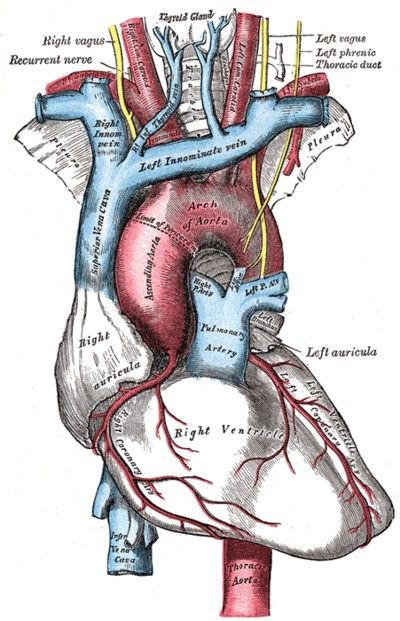
The bronchial artery is the major supply of oxygenated blood to the structures of the lung. About 1% of the blood flowing in the lung is derived from the bronchial artery. The bronchial artery is also the main supply for airways in the chest. The bronchial artery and the ductus aorta are two of the most important parts of the body.
Bronchial Arteries Supply the Lungs with Oxygen
The bronchial artery supplies the lung with oxygen. Its two branches supply the upper oesophagus and the pulmonary aorta. The smallest peripheral bronchial artery anastomoses with the pulmonary artery to form a systemic arterial system. While the bronchial artery is not a major source of collateral circulation, it is a vital organ.
Both the left and right bronchial arteries have anastomoses with the pulmonary artery. The right bronchial artery originates in the thoracic aorta, while the left bronchial artery is common to the left and the aorta. The two bronchial arteries are related. They share a similar origin with the aorta.
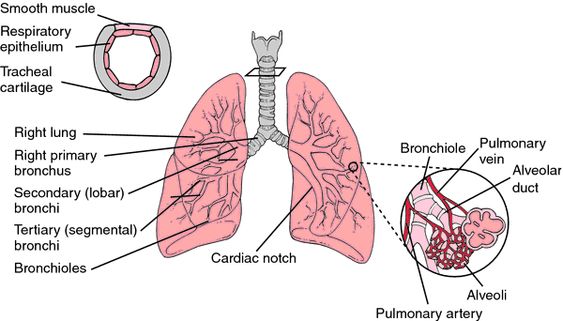
The bronchial arteries receive about 1% of the cardiac output. The remaining blood is returned to the heart through pulmonary veins. Despite being the pulmonary artery, the bronchial artery is the main artery for the airway. It is the largest of the thoracic arteries, originating from the thoracic aorta. The lungs are divided into four trunks: the inferior left bronchial artery, the intercostobrachial artery, and the superior esophagus.
Reference: