Healthbeauty123.com – Autoimmune hepatitis is a liver disease caused by an immune response to the liver. The liver is an organ that produces bile and other substances that support the body. If your liver is damaged, it can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer. Fortunately, there are tests available that can detect and diagnose this condition. These tests measure the activity of certain liver enzymes and substances. A liver biopsy can also be done to see if your liver has been affected by this disease.
Definitive Causes of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Although the exact cause of this disease has not yet been determined, it is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and immunologic factors. Some studies have linked this disease to certain drugs and infections. Several different treatments are available to treat the symptoms. For example, patients may be prescribed corticosteroids if the liver has been damaged by a viral infection.
Autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic liver disease in which the immune system attacks liver cells. The inflammation and damage caused by this disease can cause scarring and liver failure. It affects both men and women. The condition is more common in women than in men. There are several treatment options available for autoimmune hepatitis.

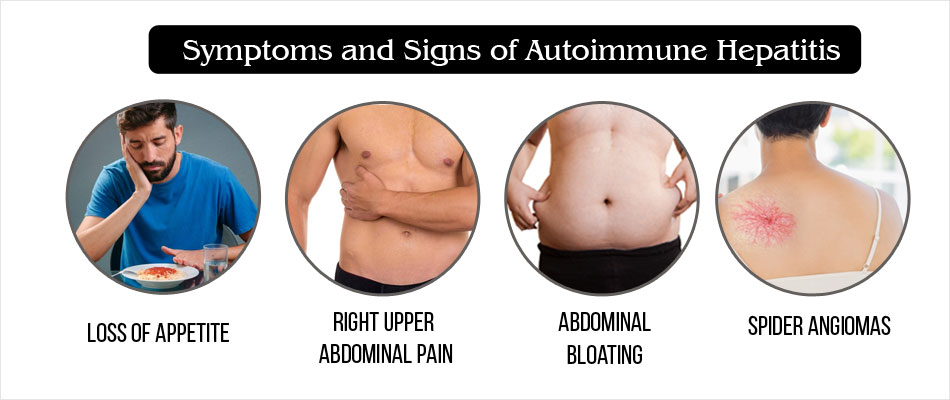
Symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis can range from mild to severe. They may include abdominal discomfort, dark urine, and aching joints. However, in more advanced cases, the disease may cause serious complications, including liver cancer and biliary infections. During early stages, medical professionals can diagnose this disease by performing blood tests. A liver ultrasound can also be performed to view the liver and determine whether or not it is affected.
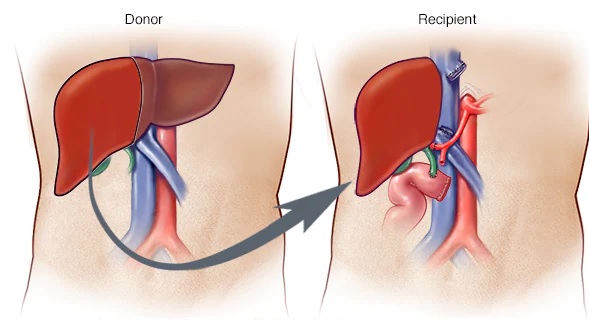
Liver Transplant Is The Best Treatment Option
There is no cure for autoimmune hepatitis, but it can be controlled with medication. Treatments often include steroids or agents that suppress the immune system. If the condition is severe, a liver transplant may be the best treatment option. Patients with autoimmune hepatitis may need to stay on medications for many years, and some may even require liver transplant surgery.
A liver biopsy is a test that confirms the diagnosis and stages the liver’s fibrosis. The biopsy involves a patient lying on a table while a doctor inserts a needle into the liver. The doctor then sends the liver tissue to a pathologist for examination under a microscope. The pathologist uses special staining techniques to confirm the diagnosis. An autoimmune hepatitis patient should be fasting for at least eight hours prior to the test.
Diagnosing Autoimmune Hepatitis involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and blood tests. Liver biopsy can also reveal signs of cirrhosis, which is another autoimmune liver disease. Doctors often treat autoimmune hepatitis with medicines that suppress the immune system. The medications most commonly used are corticosteroids and azathioprine. However, these medications are not without side effects and can cause liver failure or liver cancer.
Symptoms of Autoimmune Hepatitis Vary
Autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic disease caused by the immune system attacking the liver cells. Symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis vary, ranging from joint pain to cirrhosis. People with the disease usually experience fatigue, joint pain, poor appetite, nausea, and pain in the liver. Some people may also have jaundice. Although autoimmune hepatitis is not contagious, it can lead to other complications such as liver cancer and liver failure.
In the early stages, symptoms of AIH may be absent or mild, and the disease may only be diagnosed when the liver has developed scars. In later stages, the symptoms can become more prominent. Because the symptoms are similar to those of other autoimmune conditions, AIH is often mistaken for other diseases. However, blood tests can help identify the cause of this disease. A blood test can measure the IgG antibodies, which help the body fight inflammation and infection, to detect AIH.
Treatment for autoimmune hepatitis aims to control symptoms and slow the progression of liver damage. Treatment may involve taking a steroid drug called prednisone or an immunosuppressant called azathioprine. These medications are usually taken daily, and the dose may be reduced as the disease progresses. However, it is important to note that prednisone can cause serious side effects. Autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic liver disease caused by an immune response that targets the liver cells. Eventually, this can lead to the development of liver failure and cirrhosis. Autoimmune hepatitis affects people of any age, but it is more common in women.
Reference: